Understanding Bipolar Disorder: Symptoms, Causes, and EffectiveTreatment
The Sypmtoms Of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive illness, is a mental health condition that causes extreme shifts in mood, energy, and behavior. People with bipolar disorder experience periods of intense mania, followed by episodes of depression. These mood swings can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life and relationships.

During a manic episode, individuals with bipolar disorder may experience an elevated mood, increased energy levels, and a heightened sense of self-confidence. They may engage in impulsive and risky behaviors, such as excessive spending, reckless driving, or engaging in promiscuous activities. Their speech may become rapid and pressured, making it difficult for others to keep up with their thoughts. They may also have difficulty sleeping, feeling the need for only a few hours of rest or even going without sleep for days on end.
In contrast, during a depressive episode, individuals with bipolar disorder may feel overwhelming sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed. They may struggle with low energy levels, finding it difficult to complete even simple tasks. Their appetite may change, leading to weight loss or gain. They may experience feelings of guilt, worthlessness, or thoughts of death and suicide. Concentration and memory may become impaired, making it challenging to focus on work or school.

It is important to note that the severity and duration of these symptoms can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience more frequent and intense episodes, while others may have longer periods of stability between episodes. Additionally, the specific symptoms can also differ between individuals, making it crucial for a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional to diagnose bipolar disorder accurately.
If left untreated, bipolar disorder can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and functioning. The unpredictable shifts in mood and energy levels can strain relationships, lead to difficulties at work or school, and increase the risk of substance abuse. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals with bipolar disorder can manage their symptoms effectively and lead fulfilling lives.

Treatment for bipolar disorder often involves a combination of medication and psychotherapy. Mood stabilizers, such as lithium or anticonvulsants, are commonly prescribed to help regulate mood swings. Antidepressants may also be used during depressive episodes, but caution must be exercised to prevent triggering a manic episode. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or interpersonal therapy (IPT), can assist individuals in understanding and managing their emotions, improving coping skills, and developing strategies to prevent relapse.
In conclusion, bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that can significantly impact a person’s life. Understanding the symptoms and seeking professional help is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. With the right support and treatment plan, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead fulfilling lives and manage their symptoms to achieve stability and well-being.
Manic Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
During a manic episode, individuals with bipolar disorder may experience the following symptoms:

- Feeling extremely happy or euphoric
- Having an inflated sense of self-esteem or grandiosity
- Having a decreased need for sleep
- Talking rapidly and jumping from one idea to another
- Feeling restless or having an increased level of energy
- Engaging in risky behaviors, such as excessive spending or impulsive sexual encounters
These manic symptoms can last for a week or longer and can severely disrupt a person’s life. It’s important to note that not everyone with bipolar disorder experiences manic episodes.
During a manic episode, individuals with bipolar disorder may display a wide range of behaviors that can significantly impact their daily functioning. For example, they may exhibit a heightened sense of creativity and productivity, leading to a surge of new ideas and projects. This burst of energy and enthusiasm can be exhilarating for the individual, but it can also lead to a lack of sleep and an inability to focus on one task for an extended period of time.
In addition to the increased energy and productivity, individuals in a manic state may also experience an inflated sense of self-importance. They may believe they possess special abilities or talents that set them apart from others. This grandiosity can manifest in various ways, such as feeling invincible or believing they have a special connection to a higher power.
Furthermore, during a manic episode, individuals may have an overwhelming urge to engage in impulsive and risky behaviors. This can include reckless spending sprees, engaging in unprotected sexual encounters, or participating in dangerous activities without considering the potential consequences. These behaviors can have severe financial, social, and emotional consequences for the individual and their loved ones.
It is important to note that not all individuals with bipolar disorder experience manic episodes. Some may only experience depressive episodes, while others may have a combination of both manic and depressive episodes. The frequency, duration, and intensity of these episodes can vary greatly from person to person. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional is necessary to accurately diagnose and treat bipolar disorder.
Depressive Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
During a depressive episode, individuals with bipolar disorder may experience the following symptoms:

- Feeling sad, hopeless, or empty
- Having a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
- Experiencing significant changes in appetite or weight
- Having trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
- Feeling fatigued or lacking energy
- Having difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Having thoughts of death or suicide
- Feeling a sense of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Experiencing physical symptoms such as headaches or stomachaches
- Having difficulty in maintaining relationships or socializing
- Withdrawing from friends and family
- Experiencing a decrease in productivity or motivation
These depressive symptoms can last for weeks or months and can greatly affect a person’s ability to function in daily life. It is important to note that not everyone with bipolar disorder will experience the same symptoms or to the same degree. The severity and duration of depressive episodes can vary from person to person. It is crucial for individuals with bipolar disorder to seek professional help and receive appropriate treatment to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Hypomanic Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
In addition to manic and depressive episodes, some individuals with bipolar disorder may experience hypomanic episodes. Hypomania is a less severe form of mania and may include the following symptoms:
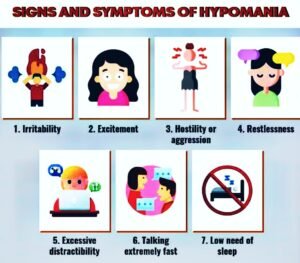
- feeling unusually energetic or irritable
- Engaging in impulsive or risky behaviors
- Having an inflated sense of self-confidence
- Talking rapidly or having racing thoughts
- Feeling restless or unable to sit still
- Experiencing an increased need for sleep
- Engaging in excessive goal-directed activities
- Feeling easily distracted or having difficulty concentrating
- Engaging in excessive spending or reckless financial decisions
- Having an increased interest in pleasurable activities, such as sex or gambling
Hypomanic episodes are typically shorter and less severe than full-blown manic episodes, but they can still have a significant impact on a person’s life. During a hypomanic episode, individuals may feel a surge of energy and creativity, leading them to take on multiple projects or tasks simultaneously. However, this increased activity can also lead to burnout or a loss of focus. Additionally, the impulsive and risky behaviors associated with hypomania can have negative consequences, such as strained relationships or financial difficulties.
It is important to note that while hypomania may not cause the same level of impairment as mania, it is still a symptom of bipolar disorder and should not be dismissed or ignored. If you or someone you know is experiencing hypomanic symptoms, it is important to seek professional help for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Effective management of bipolar disorder can help individuals lead fulfilling and balanced lives.
Other Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
In addition to the mood symptoms mentioned above, individuals with bipolar disorder may also experience other symptoms, including:

- Difficulty with memory or concentration
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Physical symptoms, such as headaches or stomachaches
- Substance abuse or addiction
- Relationship problems
- Social withdrawal
- Impulsivity and risky behavior
- Insomnia or excessive sleep
- Feelings of guilt or worthlessness
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities
- Restlessness or agitation
- Psychomotor retardation or slowed movements
- Thoughts of death or suicide
These additional symptoms can further complicate the lives of individuals with bipolar disorder, making it important for them to seek appropriate treatment and support. It’s important to remember that everyone’s experience with bipolar disorder is unique, and symptoms can vary from person to person.
Seeking Help for Bipolar Disorder

If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of bipolar disorder, it’s important to seek help from a mental health professional. A diagnosis of bipolar disorder can only be made by a qualified healthcare provider, who will conduct a thorough evaluation and may recommend treatment options such as medication, therapy, or a combination of both.
Bipolar disorder is a complex and chronic mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by extreme mood swings, ranging from manic episodes of elevated mood, energy, and activity levels to depressive episodes of low mood, decreased energy, and feelings of hopelessness. These mood swings can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
When seeking help for bipolar disorder, it’s important to find a mental health professional who specializes in mood disorders and has experience in diagnosing and treating bipolar disorder. This may include psychiatrists, psychologists, or clinical social workers. They will work with you to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and goals.
Treatment for bipolar disorder often involves a combination of medication and therapy. Medications, such as mood stabilizers, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, can help manage the symptoms and stabilize mood swings. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), can help individuals develop coping strategies, improve communication skills, and manage stress.
It’s important to remember that seeking help for mental health concerns is not a sign of weakness. In fact, it takes courage and strength to reach out for support. Bipolar disorder is a treatable condition, and with the right support and treatment, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead fulfilling and productive lives.
If you or someone you know is in crisis or experiencing thoughts of self-harm or suicide, please reach out to a helpline or emergency services immediately. There are helplines available 24/7 that can provide support, guidance, and resources in times of crisis.
Take care of your mental health and remember that you are not alone. There is a strong community of individuals with bipolar disorder who understand what you are going through and can offer support and encouragement along your journey to recovery.
Post By : www.worldwidevista.com


